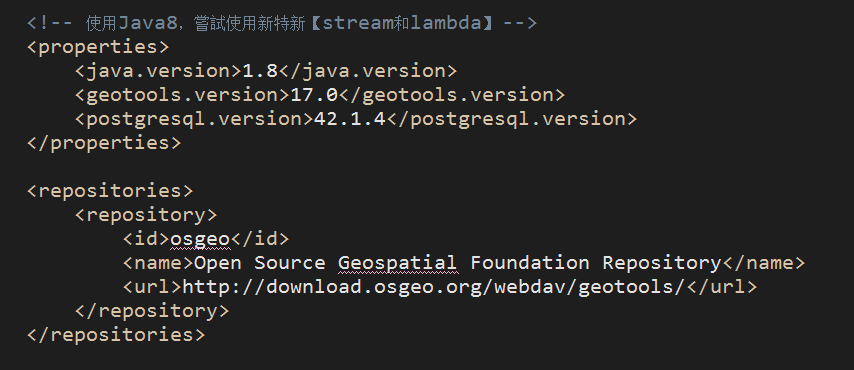
JAVA用geotools读写shape格式文件
JAVA用geotools读写shape格式文件 (对应geotools版本:2.7.2)
(后面添加对应geotools 10.0版本的写法)
读shape文件。
shape格式文件最少包含3个文件,他们的后缀是:.shp, .dbf, .shx。
.shp存储地理形状和位置信息,.dbf存储属性信息,.shx是索引文件。
单独读取DBF文件
public void readDBF(String path) {
DbaseFileReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new DbaseFileReader(new ShpFiles(path), false, Charset.forName("GBK"));
DbaseFileHeader header = reader.getHeader();
int numFields = header.getNumFields();
//迭代读取记录
while (reader.hasNext()) {
try {
Object[] entry = reader.readEntry();
for (int i=0; i<numFields; i++) {
String title = header.getFieldName(i);
Object value = entry[i];
System.out.println(title+"="+value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
//关闭
try {reader.close();} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
}
读取3个文件,以point为例:
public void readSHP(String path) {
ShapefileDataStore shpDataStore = null;
try{
shpDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(new File(path).toURI().toURL());
shpDataStore.setStringCharset(Charset.forName("GBK"));
String typeName = shpDataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> featureSource = null;
featureSource = (FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature>)shpDataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);
FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> result = featureSource.getFeatures();
System.out.println(result.size());
FeatureIterator<SimpleFeature> itertor = result.features();
while(itertor.hasNext()){
SimpleFeature feature = itertor.next();
Collection<Property> p = feature.getProperties();
Iterator<Property> it = p.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Property pro = it.next();
if (pro.getValue() instanceof Point) {
System.out.println("PointX = " + ((Point)(pro.getValue())).getX());
System.out.println("PointY = " + ((Point)(pro.getValue())).getY());
} else {
System.out.println(pro.getName() + " = " + pro.getValue());
}
}
}
itertor.close();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
写shape文件,以point为例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
//定义属性
final SimpleFeatureType TYPE = DataUtilities.createType("Location",
"location:Point," + // <- the geometry attribute: Point type
"POIID:String," + // <- a String attribute
"MESHID:String," + // a number attribute
"OWNER:String"
);
SimpleFeatureCollection collection = FeatureCollections.newCollection();
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = new GeometryFactory();
SimpleFeatureBuilder featureBuilder = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(TYPE);
double latitude = Double.parseDouble("116.123456789");
double longitude = Double.parseDouble("39.120001");
String POIID = "2050003092";
String MESHID = "0";
String OWNER = "340881";
/* Longitude (= x coord) first ! */
Point point = geometryFactory.createPoint(new Coordinate(longitude, latitude));
Object[] obj = {point, POIID, MESHID, OWNER};
SimpleFeature feature = featureBuilder.buildFeature(null, obj);
collection.add(feature);
feature = featureBuilder.buildFeature(null, obj);
collection.add(feature);
File newFile = new File("D:/newPoi.shp");
ShapefileDataStoreFactory dataStoreFactory = new ShapefileDataStoreFactory();
Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<String, Serializable>();
params.put("url", newFile.toURI().toURL());
params.put("create spatial index", Boolean.TRUE);
ShapefileDataStore newDataStore = (ShapefileDataStore) dataStoreFactory.createNewDataStore(params);
newDataStore.createSchema(TYPE);
newDataStore.forceSchemaCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
Transaction transaction = new DefaultTransaction("create");
String typeName = newDataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = newDataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);
if (featureSource instanceof SimpleFeatureStore) {
SimpleFeatureStore featureStore = (SimpleFeatureStore) featureSource;
featureStore.setTransaction(transaction);
try {
featureStore.addFeatures(collection);
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception problem) {
problem.printStackTrace();
transaction.rollback();
} finally {
transaction.close();
}
} else {
System.out.println(typeName + " does not support read/write access");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
以下代码对应geotools10.0版本
一、读shp文件(图形信息+属性信息)的写法:
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStoreFactory;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureIterator;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureSource;
import org.opengis.feature.Property;
import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeature;
public class ShpNew {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapefileDataStoreFactory dataStoreFactory = new ShapefileDataStoreFactory();
try {
ShapefileDataStore sds = (ShapefileDataStore)dataStoreFactory.createDataStore(new File("D:\\work\\shpdir\\Poi.shp").toURI().toURL());
sds.setCharset(Charset.forName("GBK"));
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = sds.getFeatureSource();
SimpleFeatureIterator itertor = featureSource.getFeatures().features();
while(itertor.hasNext()) {
SimpleFeature feature = itertor.next();
Iterator<Property> it = feature.getProperties().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Property pro = it.next();
System.out.println(pro);
}
}
itertor.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
二、读图形信息
try {
ShpFiles sf = new ShpFiles("D:\\Poi.shp");
ShapefileReader r = new ShapefileReader( sf, false, false, new GeometryFactory() );
while (r.hasNext()) {
Geometry shape = (Geometry) r.nextRecord().shape(); //com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Geometry;
System.out.println(shape.toString());
}
r.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
三、读dbf文件
public void readDBF() {
try {
FileChannel in = new FileInputStream("D:\\Poi.dbf").getChannel();
DbaseFileReader dbfReader = new DbaseFileReader(in, false, Charset.forName("GBK"));
DbaseFileHeader header = dbfReader.getHeader();
int fields = header.getNumFields();
while ( dbfReader.hasNext() ){
DbaseFileReader.Row row = dbfReader.readRow();
// System.out.println(row.toString());
for (int i=0; i<fields; i++) {
System.out.println(header.getFieldName(i) + " : " + row.read(i));
}
}
dbfReader.close();
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
四、写shape文件
public void write(String filepath) {
try {
//创建shape文件对象
File file = new File(filepath);
Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<String, Serializable>();
params.put( ShapefileDataStoreFactory.URLP.key, file.toURI().toURL() );
ShapefileDataStore ds = (ShapefileDataStore) new ShapefileDataStoreFactory().createNewDataStore(params);
//定义图形信息和属性信息
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tb = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
tb.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
tb.setName("shapefile");
tb.add("the_geom", Point.class);
tb.add("POIID", Long.class);
tb.add("NAMEC", String.class);
ds.createSchema(tb.buildFeatureType());
ds.setCharset(Charset.forName("GBK"));
//设置Writer
FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(ds.getTypeNames()[0], Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT);
//写下一条
SimpleFeature feature = writer.next();
feature.setAttribute("the_geom", new GeometryFactory().createPoint(new Coordinate(116.123, 39.345)));
feature.setAttribute("POIID", 1234567890l);
feature.setAttribute("NAMEC", "某兴趣点1");
feature = writer.next();
feature.setAttribute("the_geom", new GeometryFactory().createPoint(new Coordinate(116.456, 39.678)));
feature.setAttribute("POIID", 1234567891l);
feature.setAttribute("NAMEC", "某兴趣点2");
writer.write();
writer.close();
ds.dispose();
//读取刚写完shape文件的图形信息
ShpFiles shpFiles = new ShpFiles(filepath);
ShapefileReader reader = new ShapefileReader(shpFiles, false, true, new GeometryFactory(), false);
try {
while (reader.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(reader.nextRecord().shape());
}
} finally {
reader.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) { }
}
五、由源shape文件创建新的shape文件
public void transShape(String srcfilepath, String destfilepath) {
try {
//源shape文件
ShapefileDataStore shapeDS = (ShapefileDataStore) new ShapefileDataStoreFactory().createDataStore(new File(srcfilepath).toURI().toURL());
//创建目标shape文件对象
Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<String, Serializable>();
FileDataStoreFactorySpi factory = new ShapefileDataStoreFactory();
params.put(ShapefileDataStoreFactory.URLP.key, new File(destfilepath).toURI().toURL());
ShapefileDataStore ds = (ShapefileDataStore) factory.createNewDataStore(params);
// 设置属性
SimpleFeatureSource fs = shapeDS.getFeatureSource(shapeDS.getTypeNames()[0]);
//下面这行还有其他写法,根据源shape文件的simpleFeatureType可以不用retype,而直接用fs.getSchema设置
ds.createSchema(SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder.retype(fs.getSchema(), DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84));
//设置writer
FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(ds.getTypeNames()[0], Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT);
//写记录
SimpleFeatureIterator it = fs.getFeatures().features();
try {
while (it.hasNext()) {
SimpleFeature f = it.next();
SimpleFeature fNew = writer.next();
fNew.setAttributes(f.getAttributes());
writer.write();
}
} finally {
it.close();
}
writer.close();
ds.dispose();
shapeDS.dispose();
} catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/kaopu/article/details/84124327